Create a secret
This is an example of how to create a secret in AWS Secrets Manager and access it in a Kubernetes cluster using External Secrets.
It is a good practice to encrypt secrets using kms/config key which is created by the Infralib KMS module.
For more information about AWS Secrets Manager, see AWS Secrets Manager User Guide.
For more information about External Secrets, see External Secrets User Guide.
For more information about Secrets in Kubernetes, see Kubernetes documentation.
1. Create a secret in AWS Secrets Manager
Secrets can be created using AWS Console or AWS CLI.
1.1 Create a secret in AWS Console
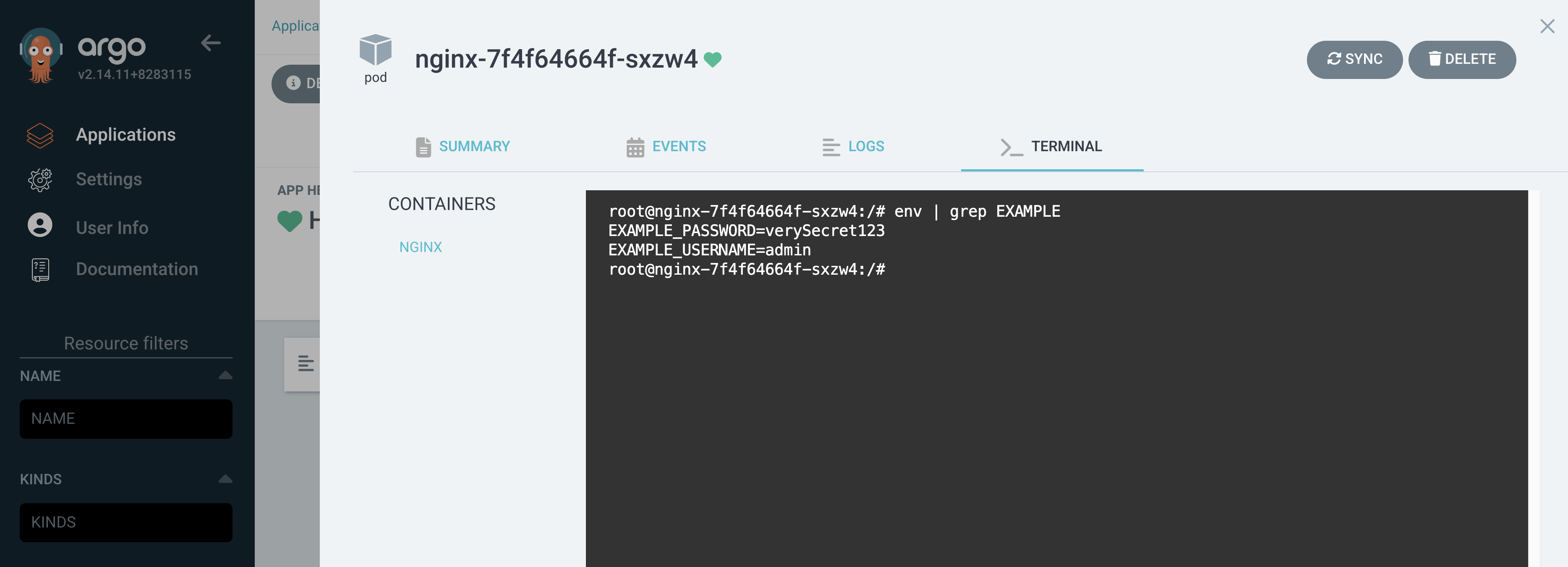
# Example secret data
EXAMPLE_USERNAME=admin
EXAMPLE_PASSWORD=verySecret123
Secrets Manager -> Store a new secret
Select Other type of secret
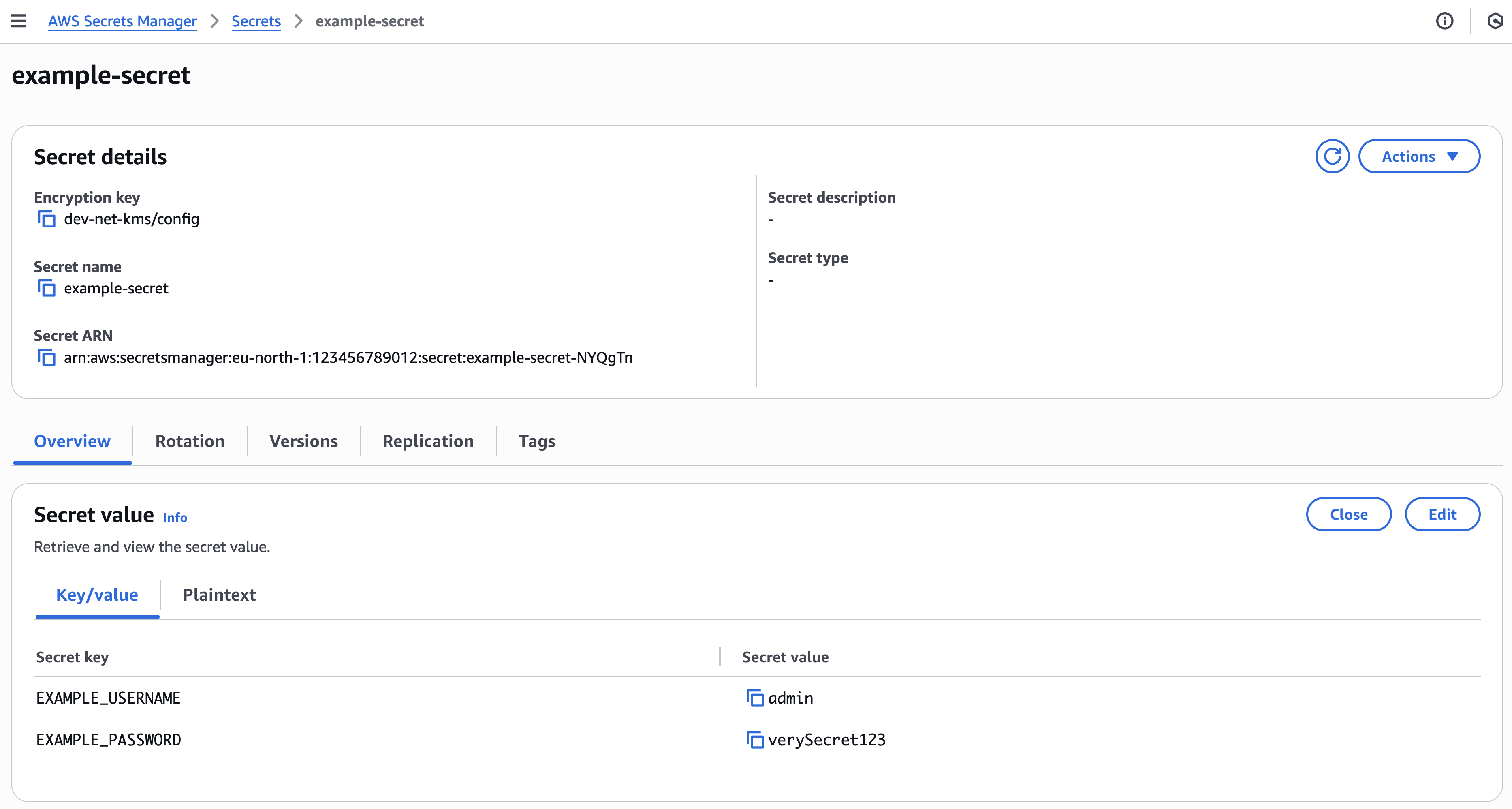
Fill Key/value pairs and choose Encryption key.
It is recommended to use kms/config key created by the Infralib KMS module.
Click Next
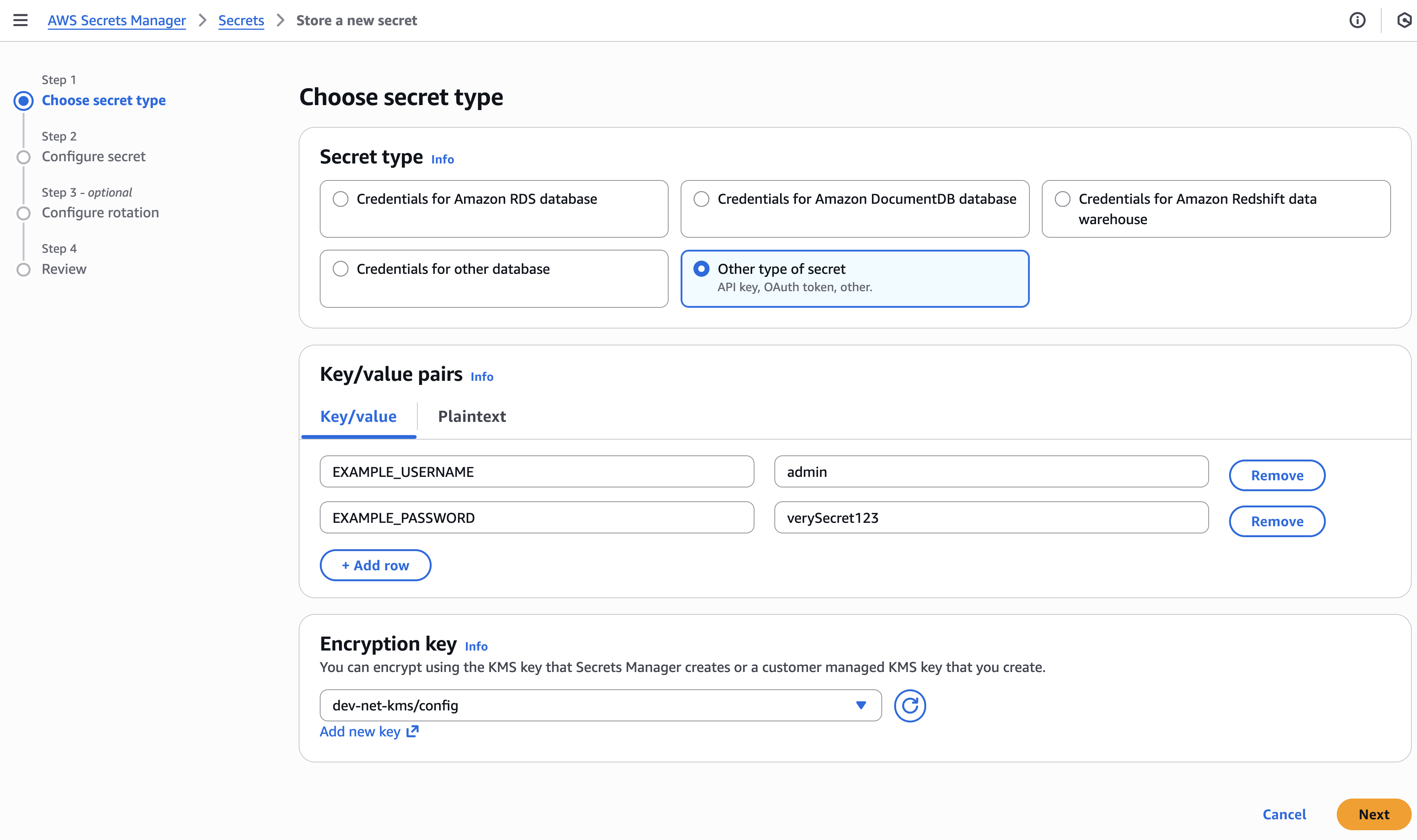
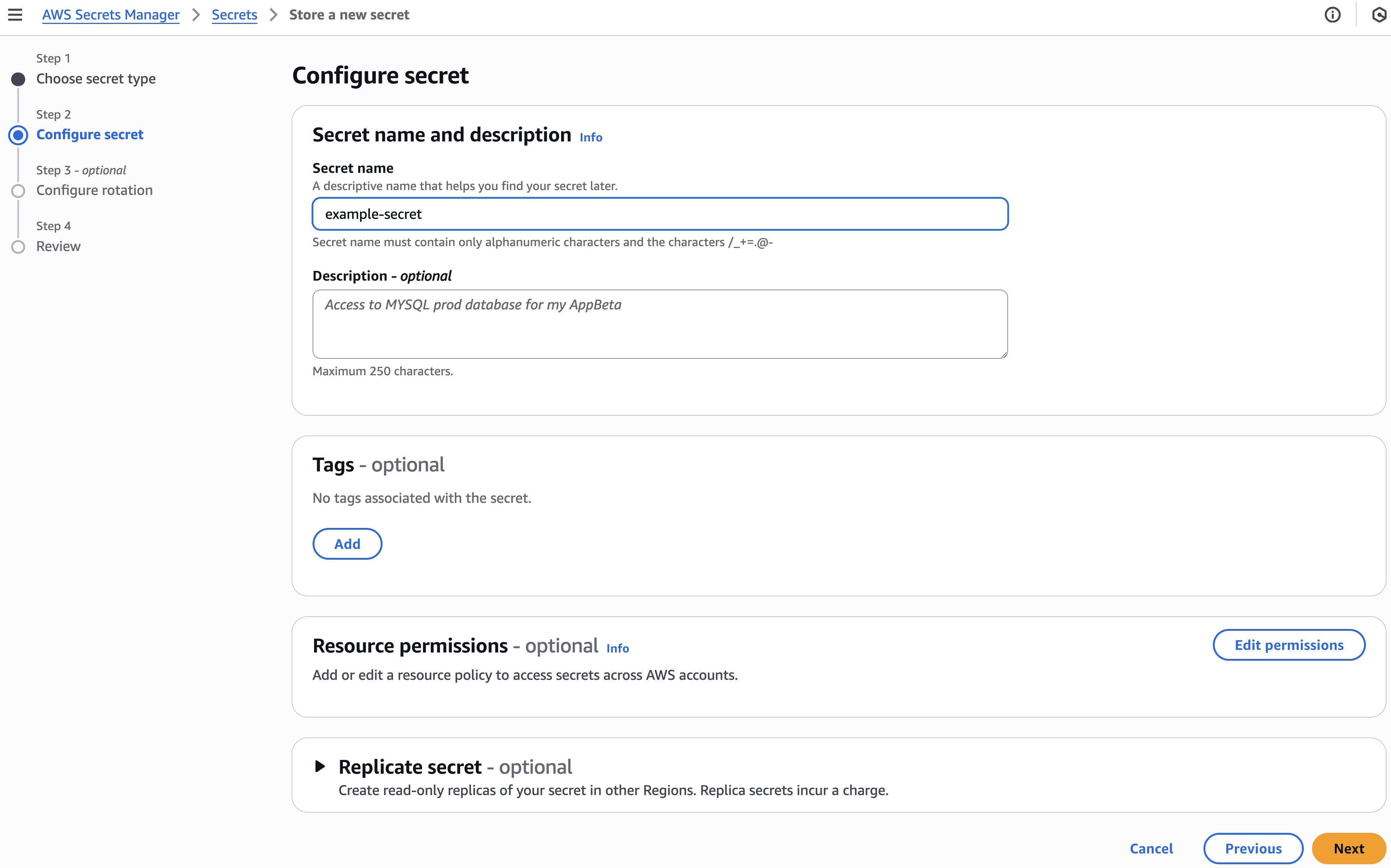
Set desired Secret name
Click Next
Verify secret exists in AWS Secrets Manager.
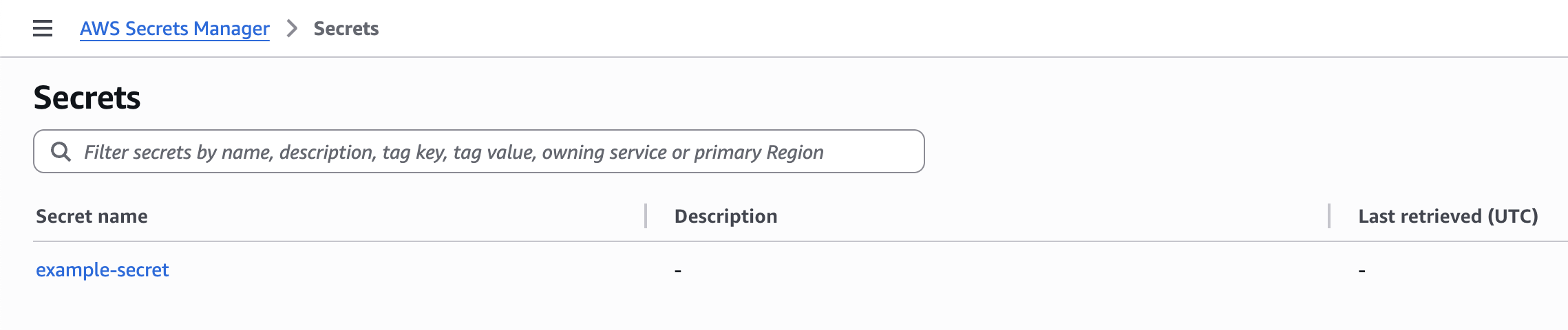
Existing secrets can be viewed and edited in AWS Console.
1.2 Create a secret in AWS CLI
aws secretsmanager create-secret \
--name example-secret \
--secret-string '{"EXAMPLE_USERNAME":"admin","EXAMPLE_PASSWORD":"verySecret123"}' \
--kms-key-id alias/dev-net-kms/config
2. Access a secret in a Kubernetes cluster with External Secrets
Secrets can be accessed in Kubernetes via ClusterSecretStore and SecretStore.
By default, a ClusterSecretStore is created by the Infralib external-secrets module.
The list of available stores can be viewed with the following command:
# Example output
$ kubectl get SecretStores,ClusterSecretStores --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME AGE STATUS CAPABILITIES READY
clustersecretstore.external-secrets.io/external-secrets 1h Valid ReadWrite True
Create an External Secret manifest and deploy it to the cluster. It is a good practice to include it in the application's Helm chart.
# Example ExternalSecret manifest to access a secret using ClusterSecretStore
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: example-secret
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: '-2'
spec:
refreshInterval: 5m
dataFrom:
- extract:
key: example-secret # AWS Secrets Manager secret
secretStoreRef:
kind: ClusterSecretStore
name: external-secrets
target:
name: example-secret # Kubernetes Secret to create
creationPolicy: Owner
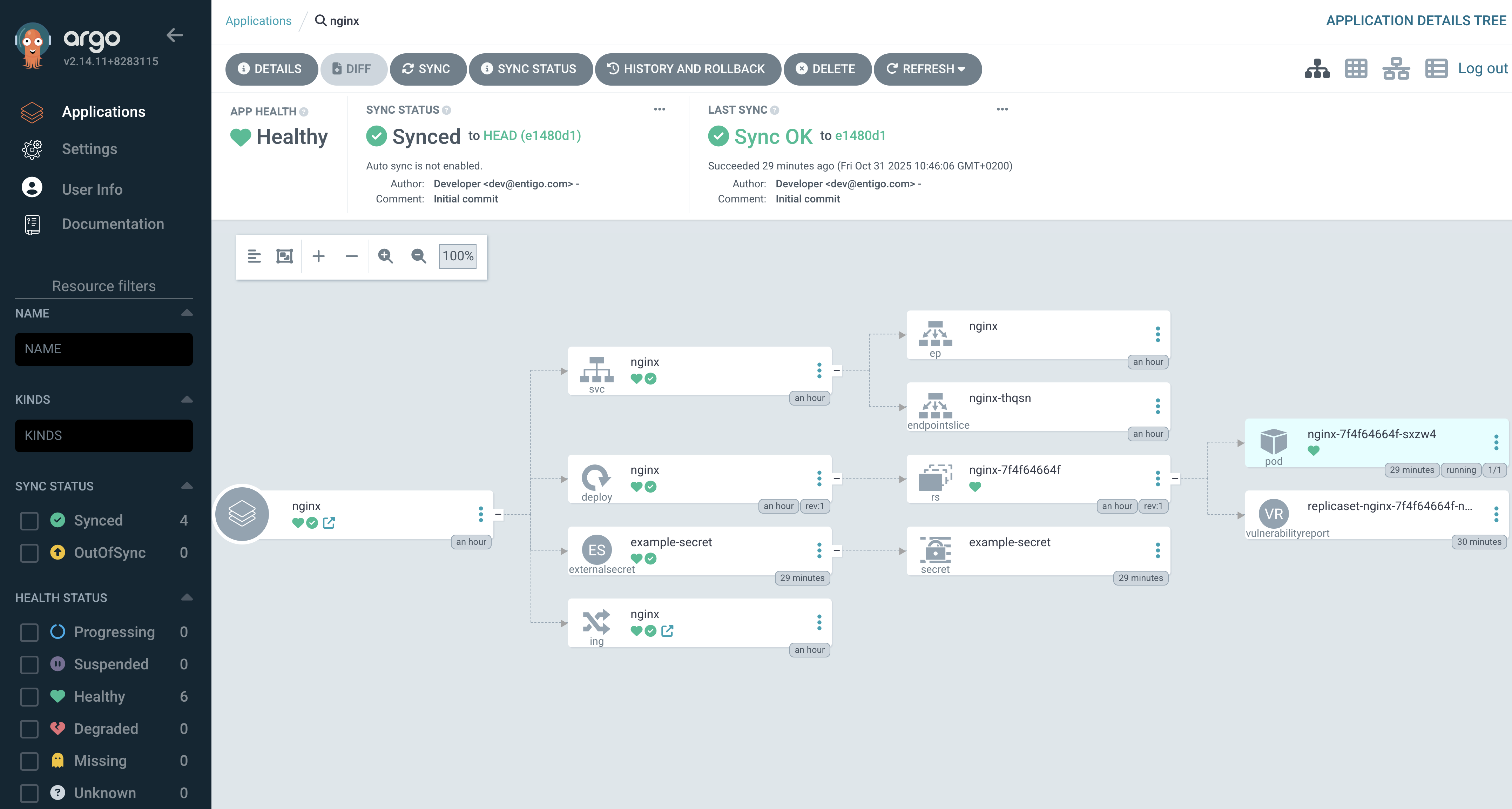
Kubernetes Secret created by External Secrets in Kubernetes
$ kubectl get secret
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
example-secret Opaque 1 10m
External Secret and Secret in ArgoCD
3. Mount a secret to a container as environment variables
# Example Deployment manifest
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: example-secret
4. Result