Create a PostgreSQL Instance
This is an example of how to create a PostgreSQLInstance, PostgreSQLUser and PostgreSQLDatabase.
1. Create Kubernetes manifests and deploy them to the cluster
Create manifests for the PostgreSQLInstance, PostgreSQLUser and PostgreSQLDatabase and deploy them to the cluster.
It is a good practice to include them in the application's Helm chart.
1.1 Create a PostgreSQLInstance manifest
Security group and security group rules to access the PostgreSQLInstance from pods are created automatically.
Connection credentials for the master user dbadmin are stored in a Kubernetes secret <.metadata.name>-dbadmin and AWS Secrets Manager secret.
# Example PostgreSQLInstance
apiVersion: database.entigo.com/v1alpha1
kind: PostgreSQLInstance
metadata:
name: example-postgresql
spec:
allocatedStorage: 20
engineVersion: '17.2'
instanceType: 'db.t3.small'
---
# Example PostgreSQLInstance with custom settings
apiVersion: database.entigo.com/v1alpha1
kind: PostgreSQLInstance
metadata:
name: example-postgresql
spec:
allocatedStorage: 20
engineVersion: '17.2'
instanceType: 'db.t3.small'
iops: 3000
multiAZ: true
parameterGroupName: 'default.postgres17'
deletionProtection: true
autoMinorVersionUpgrade: true
allowMajorVersionUpgrade: false
backupWindow: '05:00-05:00'
maintenanceWindow: 'Mon:00:00-Mon:03:00'
1.2 Create PostgreSQLUser manifest
Creating a PostgreSQLUser is required if creating a PostgreSQLDatabase. Otherwise, it is optional.
Connection credentials for users created with PostgreSQLUser manifest are stored in a Kubernetes secret <.spec.instanceRef.name>-<.metadata.name>.
To use the created user as owner for a PostgreSQLDatabase, the user must have spec.createDb and spec.createRole set to true.
# Example PostgreSQLUser
apiVersion: database.entigo.com/v1alpha1
kind: PostgreSQLUser
metadata:
name: example-user
spec:
instanceRef:
name: example-postgresql
---
# Example PostgreSQLUser with custom settings
apiVersion: database.entigo.com/v1alpha1
kind: PostgreSQLUser
metadata:
name: example-user
spec:
instanceRef:
name: example-postgresql
createDb: true
createRole: true
inherit: false
login: true
1.3 Create PostgreSQLDatabase manifest
Creating a PostgreSQLDatabase is optional.
If an user created with PostgreSQLUser manifest is used as spec.owner for a PostgreSQLDatabase, the user must have spec.createDb and spec.createRole set to true.
# Example PostgreSQLDatabase
apiVersion: database.entigo.com/v1alpha1
kind: PostgreSQLDatabase
metadata:
name: example-database
spec:
owner: example-user
instanceRef:
name: example-postgresql
---
# Example PostgreSQLDatabase with custom settings
apiVersion: database.entigo.com/v1alpha1
kind: PostgreSQLDatabase
metadata:
name: example-database
spec:
owner: example-user
instanceRef:
name: example-postgresql
extensions:
- postgis
2. Mount connection credentials to a container
Connection credentials for the master user dbadmin are stored in a Kubernetes secret <.metadata.name>-dbadmin and AWS Secrets Manager secret.
Connection credentials for users created with PostgreSQLUser manifest are stored in a Kubernetes secret <.spec.instanceRef.name>-<.metadata.name>.
For more information about Secrets in Kubernetes, see Kubernetes documentation.
# Example
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: postgres
spec:
containers:
- name: postgres
image: postgres:alpine
command: ['sleep', 'infinity']
env:
- name: PGHOST
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: example-postgresql-example-user
key: endpoint
- name: PGPORT
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: example-postgresql-example-user
key: port
- name: PGUSER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: example-postgresql-example-user
key: username
- name: PGPASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: example-postgresql-example-user
key: password
- name: PGSSLMODE
value: 'require'
3. Result
3.1 PostgreSQLInstance, PostgreSQLUser and PostgreSQLDatabase
PostgreSQLInstance, PostgreSQLUser and PostgreSQLDatabase created in Kubernetes
$ kubectl get pginstances.database.entigo.com
NAME SYNCED READY COMPOSITION AGE
example-postgresql True True pginstances.database.entigo.com 52m
$ kubectl get postgresqlusers.database.entigo.com
NAME SYNCED READY COMPOSITION AGE
example-user True False postgresqlusers.database.entigo.com 20m
$ kubectl get postgresqldatabases.database.entigo.com
NAME SYNCED READY COMPOSITION AGE
example-database True True postgresqldatabases.database.entigo.com 16m
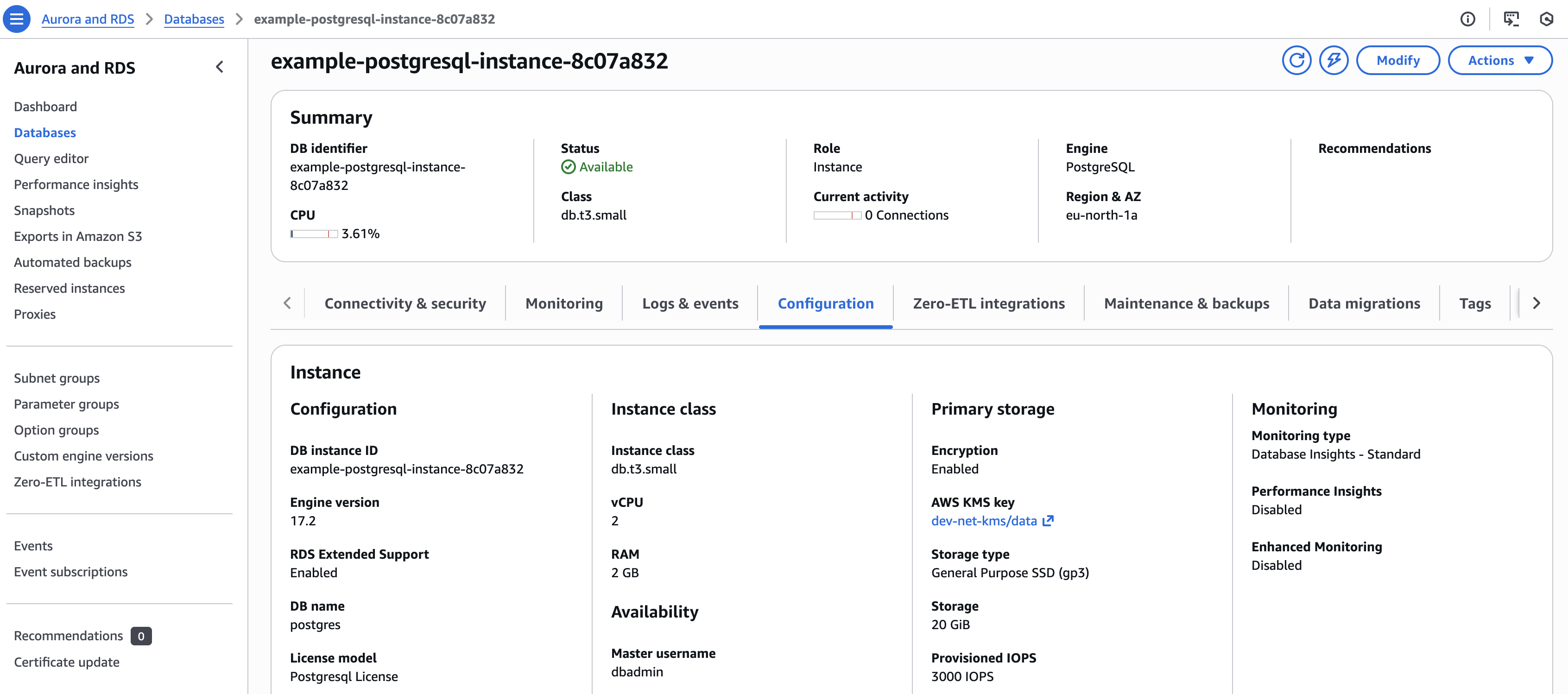
Amazon RDS PostgreSQL instance created in AWS Console
3.2 Secrets with connection credentials in Kubernetes and AWS Secrets Manager
Kubernetes secrets with connection credentials
$ kubectl get secret
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
example-postgresql-dbadmin Opaque 4 52m
example-postgresql-example-user connection.crossplane.io/v1alpha1 4 20m
$ kubectl get secret example-postgresql-dbadmin -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-postgresql-dbadmin
namespace: <namespace>
type: Opaque
data:
endpoint: <base64-encoded-endpoint>
port: <base64-encoded-port>
username: <base64-encoded-username>
password: <base64-encoded-password>
$ kubectl get secret example-postgresql-example-user -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-postgresql-example-user
namespace: <namespace>
type: Opaque
data:
endpoint: <base64-encoded-endpoint>
port: <base64-encoded-port>
username: <base64-encoded-username>
password: <base64-encoded-password>
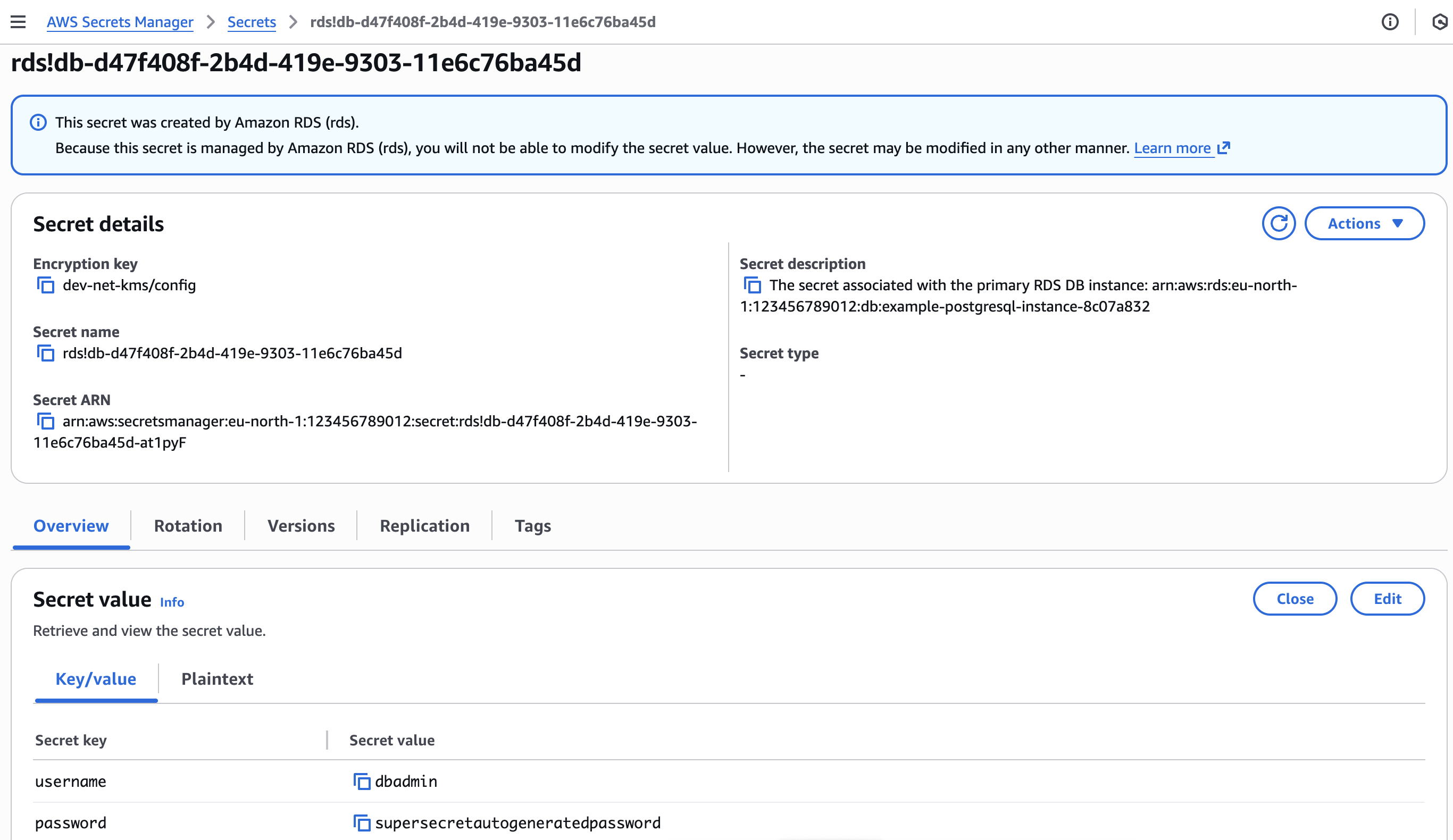
AWS Secrets Manager secret with connection credentials for dbadmin user.
3.3 Secrets mounted to a container
# Example
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
postgres 1/1 Running 0 24s
$ kubectl exec -it postgres -- bash
postgres:/# env
PGPORT=5432
PGPASSWORD=supersecretautogeneratedpassword
PGSSLMODE=require
PGUSER=example-user
PGHOST=example-postgresql-instance-8c07a832.abc123.eu-north-1.rds.amazonaws.com
postgres:/# psql example-database
psql (18.1, server 17.2)
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off, ALPN: postgresql)
Type "help" for help.
example-database=> \du
List of roles
Role name | Attributes
-----------------+------------------------------------------------------------
dbadmin | Create role, Create DB +
| Password valid until infinity
example-user | No inheritance, Create role, Create DB
...
example-database=> \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Locale Provider | Collate | Ctype | Locale | ICU Rules | Access privileges
------------------+--------------+----------+-----------------+-------------+-------------+--------+-----------+-----------------------
example-database | example-user | UTF8 | libc | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | |
postgres | dbadmin | UTF8 | libc | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | |
...
example-database=> \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Default version | Schema | Description
---------+---------+-----------------+------------+------------------------------------------------------------
plpgsql | 1.0 | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
postgis | 3.5.0 | 3.5.0 | public | PostGIS geometry and geography spatial types and functions
(2 rows)